How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that blends technical understanding with responsible practice. This guide provides a structured approach, from understanding basic drone components and pre-flight checks to mastering advanced flight maneuvers and capturing stunning aerial footage. We’ll cover everything you need to know to confidently take to the skies, ensuring both your safety and the integrity of your drone.
We’ll explore the intricacies of drone technology, covering various components and their functions, different battery types, and essential safety procedures. The guide will then delve into practical flight instructions, including takeoff and landing techniques, basic and advanced maneuvers, and camera operation for optimal image capture. Finally, we’ll address crucial legal and regulatory aspects to ensure compliance with local drone laws.
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and their functions is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will cover the major parts of a typical drone, define common terminology, and compare different battery types.
Drone Components and Their Functions
A drone comprises several key components working in harmony. Each plays a vital role in its flight capabilities and overall performance. Let’s explore these crucial elements.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate thrust, enabling the drone to take off, move, and hover. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors spin the propellers, converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy. Brushless motors are common in modern drones due to their efficiency and longevity.
- Flight Controller: This is the “brain” of the drone, responsible for processing data from various sensors (like gyroscopes, accelerometers, and barometers) and controlling the motors to maintain stability and execute commands from the remote controller.
- Battery: The power source for the drone’s motors and electronics. Battery life significantly impacts flight time. Different types of batteries offer varying capacities and performance characteristics.
- GPS Module: Provides location data, enabling features like autonomous flight, return-to-home functionality, and geofencing.
- Radio Transmitter/Receiver: The transmitter, held by the pilot, sends commands to the receiver on the drone, enabling control of its movements and functions.
- Camera (Optional): Many drones incorporate cameras for capturing aerial photos and videos. These cameras often have adjustable settings like ISO, shutter speed, and aperture.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology will enhance your understanding and interaction with your drone and the drone community.
- Altitude Hold: A flight mode that maintains a constant altitude.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mount for the camera, minimizing camera shake during flight.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): A feature that allows the drone to automatically return to its takeoff point.
- Geofencing: Setting virtual boundaries to restrict the drone’s flight area.
- Payload: The weight carried by the drone, such as a camera or other equipment.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of each motor individually.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different battery types offer distinct advantages and disadvantages. The choice depends on factors like flight time requirements and budget.
| Type | Voltage | Capacity (mAh) | Advantages/Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo (Lithium Polymer) | 3.7V per cell (typically 3S-6S configurations) | Varies widely (500mAh – 5000mAh+) | High power density, lightweight; requires careful handling, can be dangerous if mishandled. |
| LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage) | 4.35V per cell | Varies widely (500mAh – 5000mAh+) | Higher voltage than LiPo, increased flight time; more expensive than LiPo. |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist and adherence to safety procedures are paramount for safe and responsible drone operation. Neglecting these steps can lead to accidents and damage.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, meticulously check your drone and its components to ensure everything is in order and ready for flight. This will prevent unexpected issues during your flight.
- Battery Check: Verify battery charge level and condition. Ensure proper connection.
- Propeller Inspection: Examine propellers for damage or cracks. Replace if necessary.
- GPS Signal Verification: Confirm a strong GPS signal before takeoff. Sufficient satellites are needed for accurate positioning.
- Motor and ESC Function Test: Briefly power on the drone to test motor responsiveness.
- Camera Check (if applicable): Ensure the camera is properly mounted and functioning.
- Remote Controller Check: Verify controller batteries and connection.
- Environment Check: Assess weather conditions (wind speed, visibility) and surrounding environment for potential hazards.
Safe Drone Operation Procedures
Responsible drone operation involves adhering to established safety guidelines to prevent accidents and maintain a safe airspace.
- Maintain Visual Line of Sight (VLOS): Keep the drone within your direct line of sight at all times.
- Avoid Flying Near Airports or Restricted Airspace: Check local regulations and airspace restrictions before flying.
- Respect Privacy: Do not fly over private property without permission.
- Be Aware of Obstacles: Maintain awareness of your surroundings and avoid flying near obstacles.
- Fly Responsibly: Avoid reckless maneuvers that could endanger people or property.
Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual flowchart aids in systematically conducting the pre-flight inspection.
The flowchart would visually represent the checklist above, with each step leading to the next, culminating in a “Ready to Fly” decision point. If any step fails the check, a “Troubleshooting” branch would initiate.
Taking Off and Landing

Safe and controlled takeoff and landing procedures are essential for preserving the integrity of your drone and ensuring a successful flight. These maneuvers should be practiced to achieve precision and confidence.
Safe Takeoff Procedures
A smooth and controlled takeoff is crucial for a successful flight. Calibration and flight mode selection play vital roles.
- Calibration: Calibrate the drone’s compass and IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Flight Mode Selection: Choose an appropriate flight mode (e.g., Stabilize, Altitude Hold, GPS mode) based on your experience and the environment.
- Throttle Control: Gradually increase the throttle to lift the drone smoothly and steadily off the ground.
- Hovering: Once airborne, practice maintaining a stable hover before proceeding with other maneuvers.
Safe Landing Procedures
A precise landing minimizes the risk of damage to the drone. Smooth and controlled descent is crucial.
- Controlled Descent: Gradually lower the throttle to descend slowly and steadily.
- Gentle Touchdown: Aim for a soft landing to avoid sudden impacts.
- Power Down: After a safe landing, switch off the drone’s power.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques Comparison
Different techniques offer varying levels of control and assistance.
- Assisted Takeoff: The drone assists in the takeoff process, making it easier for beginners. This often involves automated altitude hold and stability features.
- Manual Takeoff: Requires more skill and control from the pilot. This involves manually controlling the throttle and maintaining stability.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the functions of the control sticks and executing basic maneuvers are fundamental to piloting a drone effectively and safely. Mastering these basics forms the foundation for more advanced techniques.
Flight Control Stick Functions, How to operate a drone
The control sticks on a typical drone remote typically control four axes of movement.
- Left Stick (Throttle/Altitude): Controls altitude (up/down) and throttle (forward/backward movement).
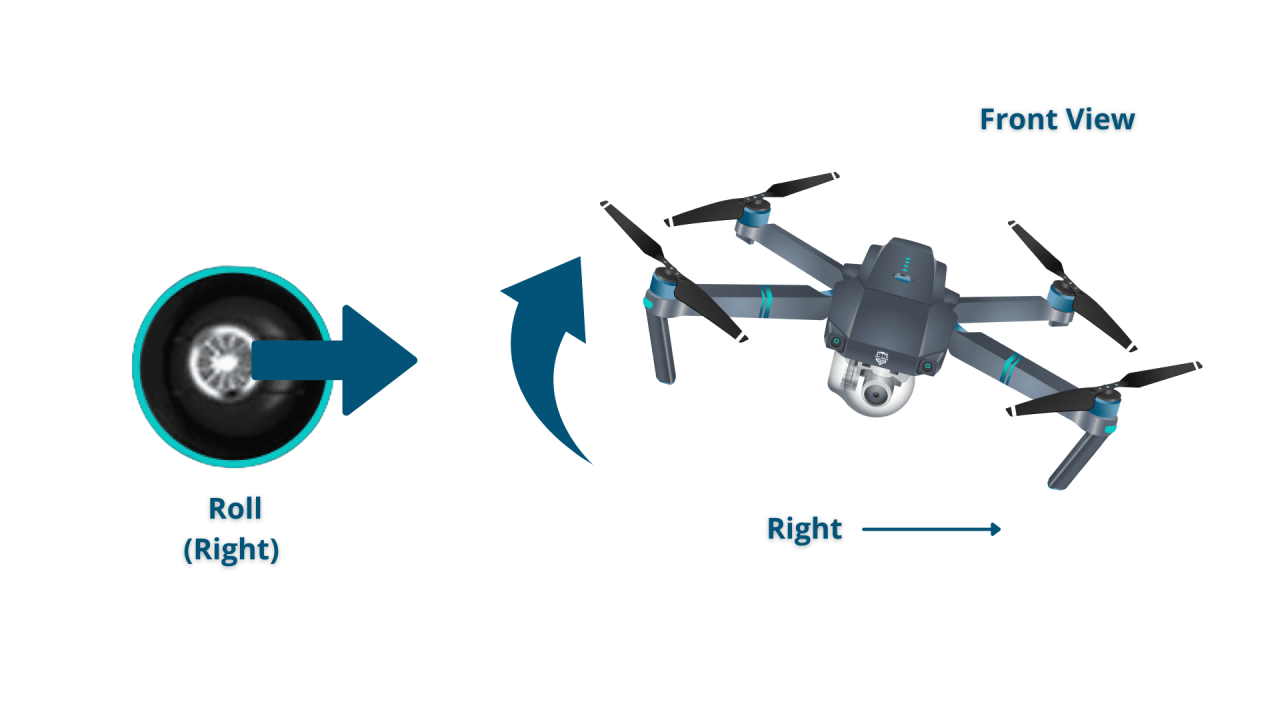
- Right Stick (Yaw/Roll/Pitch): Controls yaw (rotation), roll (side-to-side tilt), and pitch (forward/backward tilt).
Basic Flight Maneuvers

Practicing these maneuvers builds confidence and control.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Moving Forward/Backward: Using the left stick to control throttle.
- Moving Sideways (Strafe): Using the right stick to control roll.
- Rotating (Yaw): Using the right stick to control yaw.
Maintaining Stable Flight in Various Wind Conditions
Wind significantly affects drone stability. Here’s how to adapt your flying techniques.
- Increased Throttle: In windy conditions, you may need to increase throttle to compensate for wind resistance.
- Small, Precise Adjustments: Make small, precise adjustments to the control sticks to counteract wind gusts.
- Angle Adjustments: Adjust the drone’s angle slightly to counter wind direction.
- Consider Landing: In strong winds, it’s best to land the drone to avoid potential damage or loss of control.
Advanced Flight Techniques
Advanced flight techniques enhance a pilot’s skills, enabling precise control and navigation in complex environments. These techniques demand practice and a thorough understanding of drone dynamics.
Flying in Confined Spaces
Navigating tight spaces requires precise control and awareness.
- Slow and Deliberate Movements: Avoid abrupt movements to prevent collisions.
- Careful Observation: Constantly scan the environment for obstacles.
- Use of Low-Speed Modes: Utilize lower speed settings to enhance control.
Navigating Obstacles and Maintaining Situational Awareness
Maintaining awareness of surroundings is crucial to safe operation.
- Visual Inspection: Regularly check your surroundings for potential obstacles.
- Obstacle Avoidance Systems (if available): Utilize any built-in obstacle avoidance features.
- Strategic Flight Paths: Plan your flight path to avoid obstacles.
Tips for Improving Drone Piloting Skills
Continuous practice and understanding drone dynamics improve piloting skills.
- Practice Precision Maneuvers: Regularly practice hovering, precise movements, and smooth transitions.
- Understand Wind Effects: Learn to anticipate and compensate for wind conditions.
- Simulators: Use drone simulators to practice flying in various conditions without risk.
- Study Flight Theory: Learn about aerodynamics and drone control systems.
Drone Camera Operation and Image Capture
Understanding drone camera settings and techniques is crucial for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos. This section covers essential camera settings and composition techniques.
Drone Camera Settings and Functions
Camera settings significantly impact image quality. Adjustments depend on lighting and desired effect.
- ISO: Controls the sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values are better in bright conditions, while higher ISO values are needed in low light, but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Determines how long the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds blur motion (useful for waterfalls or flowing water).
- Aperture: Controls the size of the lens opening, affecting depth of field. A wider aperture (lower f-number) creates a shallow depth of field, blurring the background.
- White Balance: Adjusts the colors to accurately represent the scene’s lighting conditions.
Capturing High-Quality Photos and Videos
Achieving high-quality aerial media requires attention to detail.
- Proper Lighting: Avoid harsh shadows and direct sunlight.
- Steady Shots: Use the gimbal to stabilize the camera and prevent shake.
- Optimal Settings: Adjust camera settings based on lighting conditions and desired effects.
Creative Camera Angles and Shot Compositions
Experimenting with angles and composition enhances the visual appeal.
- High-Angle Shots: Provide a wide overview of the scene.
- Low-Angle Shots: Emphasize size and scale.
- Dutch Angle Shots: Create a sense of unease or drama.
- Rule of Thirds: Place key elements along imaginary lines dividing the frame into thirds.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting: How To Operate A Drone
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for prolonging the lifespan of your drone and ensuring its optimal performance. This section will cover routine maintenance procedures and common troubleshooting techniques.
Routine Maintenance Procedures
Regular maintenance keeps your drone flying smoothly.
Understanding drone operation involves several key steps, from pre-flight checks to mastering the controls. Successfully navigating the airspace requires careful planning and adherence to regulations. For a comprehensive guide covering all aspects, including safety procedures and legal requirements, consult this excellent resource on how to operate a drone. This will help ensure you can confidently and safely operate your drone.
Ultimately, responsible drone operation is paramount.
- Propeller Cleaning: Regularly clean propellers to remove dirt and debris.
- Motor Mount Inspection: Check motor mounts for tightness and damage.
- Battery Care: Store batteries properly and avoid overcharging or deep discharging.
- Body Inspection: Inspect the drone’s body for damage or cracks.
Common Drone Problems and Solutions
Understanding common issues and their solutions will help you resolve problems efficiently.
| Malfunction | Cause | Solution | Prevention |
|---|---|---|---|
| Drone won’t power on | Low battery, faulty battery, power switch issue | Check battery, replace battery, check power switch | Regular battery checks, careful handling |
| GPS signal lost | Obstructed signal, low satellite count | Move to an open area, wait for sufficient satellites | Fly in open areas |
| Motor malfunction | Damaged motor, loose connection | Inspect motor, tighten connections | Regular inspections |
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to local drone regulations is crucial for safe and legal operation. This section covers important legal aspects of drone ownership and operation.
Importance of Adhering to Local Drone Regulations
Understanding and obeying drone laws protects the public and ensures responsible airspace management.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone , which covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers. Mastering these skills ensures safe and responsible drone operation.
- Safety: Regulations are designed to prevent accidents and protect people and property.
- Airspace Management: Regulations help manage air traffic and prevent conflicts.
- Legal Compliance: Failing to comply can lead to fines or legal action.
Drone Registration and Permit Requirements
Registration and permits are often necessary, depending on the drone’s size, use, and location.
- Registration: Many countries require registration of drones above a certain weight.
- Permits: Special permits may be required for commercial operations or flights in restricted airspace.
- Local Regulations: Check with your local aviation authority for specific requirements.
Resources for Finding Information on Drone Laws and Regulations
Numerous resources provide up-to-date information on drone regulations.
- National Aviation Authorities: Check the website of your country’s aviation authority.
- Local Government Websites: Many local governments have information on drone regulations.
- Drone Industry Associations: Industry associations often provide resources and updates on regulations.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a combination of theoretical knowledge and hands-on practice. By understanding the fundamentals of drone components, adhering to safety protocols, and mastering flight techniques, you can unlock the potential of aerial photography and videography. Remember to always prioritize safety and responsible flying, respecting airspace regulations and the environment. With consistent practice and a keen eye for detail, you’ll soon be capturing breathtaking aerial perspectives with confidence and skill.
Commonly Asked Questions
What is the maximum flight time of a typical drone?
Flight time varies greatly depending on the drone model, battery size, and flight conditions (wind, temperature). Expect anywhere from 15 to 30 minutes on a single charge, but always check your specific drone’s specifications.
How do I know if my drone’s GPS signal is strong enough?
Most drones display GPS signal strength on their controller screen. Look for a strong signal indicator (usually a series of bars or satellites) before attempting takeoff. A weak signal can lead to unstable flight or loss of control.
What should I do if my drone loses connection?
If connection is lost, most drones have a “return-to-home” (RTH) function that will automatically guide it back to its starting point. If RTH fails, try to visually locate your drone and retrieve it safely.
How often should I calibrate my drone’s compass?
It’s good practice to calibrate your drone’s compass before each flight, especially if you’re flying near magnetic interference (power lines, metal objects). Refer to your drone’s manual for specific calibration instructions.
